

- #ANDROID CHECK FOR MALWARE HOW TO#
- #ANDROID CHECK FOR MALWARE INSTALL#
- #ANDROID CHECK FOR MALWARE FULL#
- #ANDROID CHECK FOR MALWARE ANDROID#
- #ANDROID CHECK FOR MALWARE SOFTWARE#
#ANDROID CHECK FOR MALWARE INSTALL#
Malware can steal your information, make your device send SMS messages to premium rate text services, or install adware that forces you to view web pages or download apps. Malware is designed to generate revenue for cybercriminals.
#ANDROID CHECK FOR MALWARE ANDROID#
What can viruses and other malware do to Android phones?

The virus may then be able to insert new, malicious code on your device that can monitor and manipulate your online activity. A cybercriminal may be able to install a virus on your device without your knowledge or consent. Viruses are a particular type of malware that infiltrate a computer or other device and their programs. Written with the intent to cause harm, malware can include viruses, computer worms, Trojans, ransomware, and spyware.Ĭybercriminals can use malware to access your personal data and, in some cases, subsequently use that sensitive information to commit identity theft or fraud.
#ANDROID CHECK FOR MALWARE SOFTWARE#
Malware is malicious software that can sneak onto your phone. Tips to help protect your Android device against viruses and other malware Viruses and other types of malware
#ANDROID CHECK FOR MALWARE HOW TO#
How to remove viruses and other malware from your Android device How to check for viruses and other malware on your Android phone Signs your Android phone may have a virus or other malware make sure you’ve running an updated security software on your device (usually will come pre-installed when you buy a new device).What can viruses and other malware do to Android phones?.be cautious when clicking on links that could be a phishing attempt, and.not install random apks downloaded online,.only download from the Google Play store or trusted sources only,.To avoid this kind of malware (or similar kind), you should: Change your Google (Gmail) passwords immediately.īeware of the following fake apps infected by Gooligan.The process is called flashing, which is a technical thing so we recommend you find a certified technician or go to your mobile service provider to re-flash your device. A clean installation of Android operating system on your mobile device is required.If your mobile device infected, do the following: “As part of our ongoing efforts to protect users from the Ghost Push family of malware, we’ve taken numerous steps to protect our users and improve the security of the Android ecosystem overall.” How do I know if I am infected?Ĭheck Point has offered a free online tool for affected users to check if their Google account has been infected, visit.
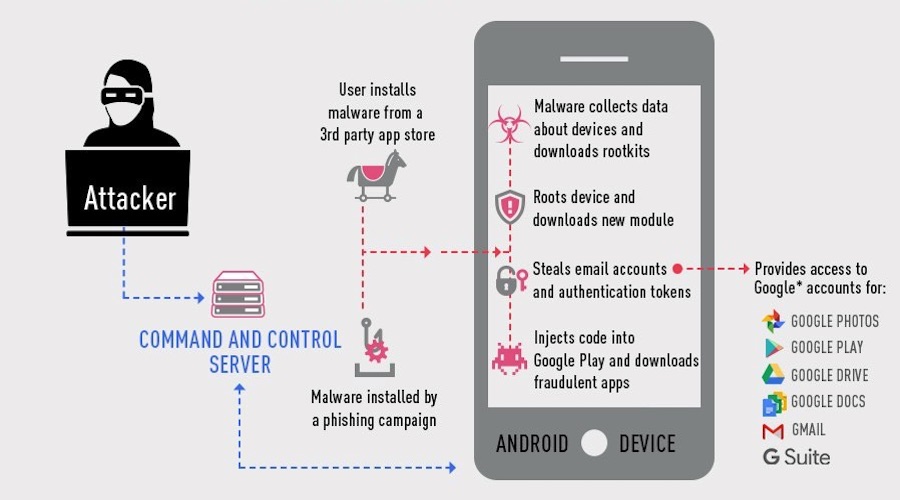
“We’re appreciative of both Check Point’s research and their partnership as we’ve worked together to understand these issues,” Google’s director of Android security Adrian Ludwig told the researchers. Then the malware leaves a positive review and a high rating on Google Play using content it receives from the C&C server.Ĭheck Point said it believes this is the “largest Google Account breach to date” and said it has alerted Google to the problem. After an app is installed, the ad service pays the attacker. The module allows Gooligan to:Īd servers, which don’t know whether an app using its service is malicious or not, send Gooligan the names of the apps to download from Google Play. This module injects code into running Google Play or GMS (Google Mobile Services) to mimic user behavior so Gooligan can avoid detection, a technique first seen with the mobile malware HummingBad.
#ANDROID CHECK FOR MALWARE FULL#
If rooting is successful, the attacker has full control of the device and can execute privileged commands remotely.Īfter achieving root access, Gooligan downloads a new, malicious module from the C&C server and installs it on the infected device. These exploits still plague many devices today because security patches that fix them may not be available for some versions of Android, or the patches were never installed by the user. Gooligan then downloads a rootkit from the C&C server that takes advantage of multiple Android 4 and 5 exploits including the well-known VROOT (CVE-2013-6282) and Towelroot (CVE-2014-3153). After an infected app is installed, it sends data about the device to the campaign’s Command and Control (C&C) server. Our research team has found infected apps on third-party app stores, but they could also be downloaded by Android users directly by tapping malicious links in phishing attack messages. The infection begins when a user downloads and installs a Gooligan-infected app on a vulnerable Android device. In a blog post published Wednesday morning, Check Point researchers wrote: How Gooligan works Image Credit: Check Point The majority of infected accounts, 57% are in Asia, 19% of accounts coming from the Americas, 9% are in Europe and 15% are in Africa. According to the research, a device infected by Gooligan is potentially granting access to data stored in any of Google’s applications including Google Docs, Google Drive, Google Photos, Gmail and Google Play.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
